
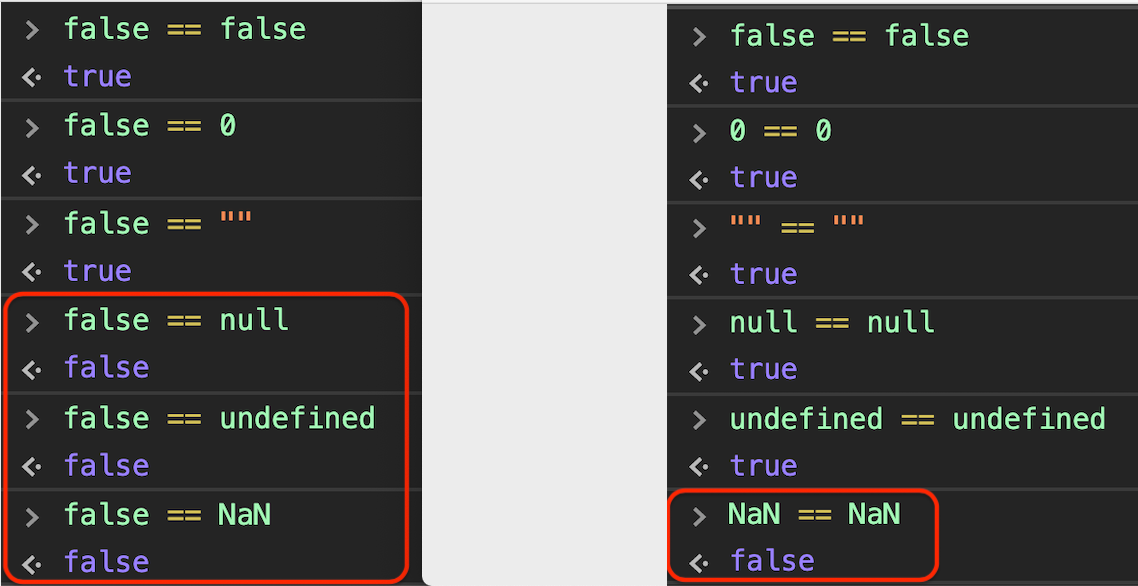
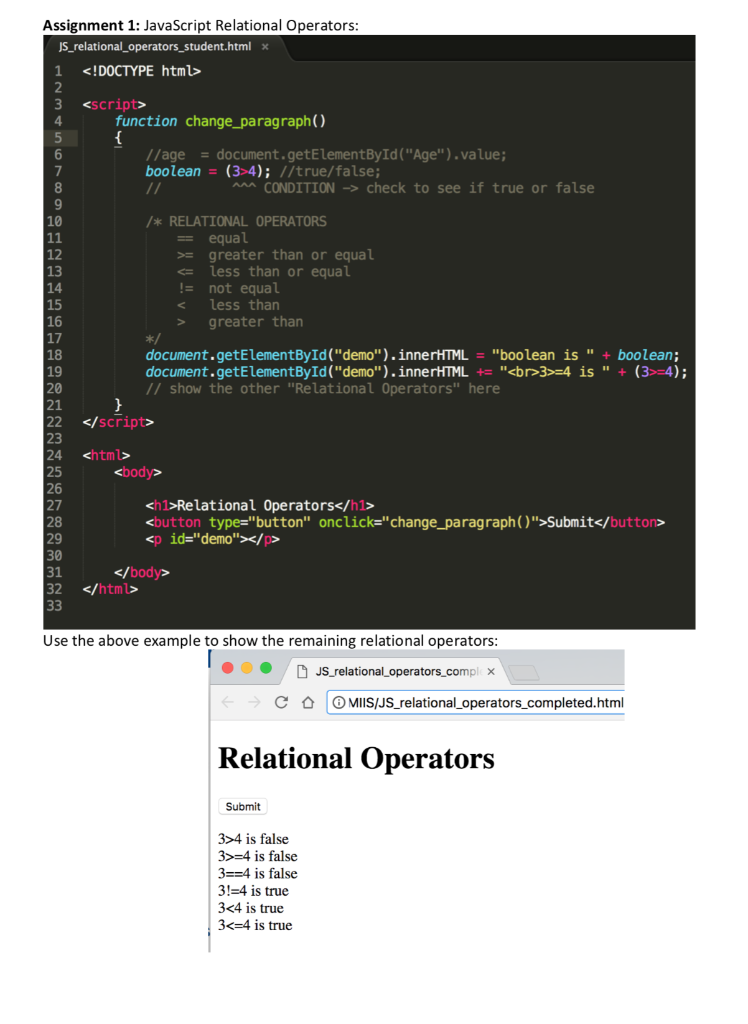
Ī = 2, b = 5, calculate c = a + b, and display c:ĭocument.getElementById("demonstration").innerHTML = c The sum of the value of variable “a” and “b” is 7. We are adding and printing their values using a third variable, “c”. In the below program, there are two variables “a” and “b”. Lastly, If both variable values are numbers, they are considered equal if both are not NaN (Not a Number) and are the same value.If the variable are of the same type, are not numeric, and have the same value, they are considered as equal.If the variable values are of different types, then the values are considered as unequal.Value are not implicitly converted to some other value before comparison.Strict equality = checks that two values are the same or not.You can use = operator in order to compare the identity of two operands even though, they are not of a similar type. It checks whether its two operands are the same or not by changing expression from one data type to others. That is, a = b assigns the value of b to a. The basic assignment operator is =, that assigns the value of one operand to another. = JavaScript operator assigns a value to the left operand depends on the value of operand available on the right side. Here are the important uses of = in JavaScript: If we compare 2 with “2” using =, then it will return a false value. This operator performs type casting for equality. = (Triple equals) is a strict equality comparison operator in JavaScript, which returns false for the values which are not of a similar type. A string with no numeric value is converts to NaN (Not a Number), which returns false. An empty string is always converts to zero. So, when you compare string with a number, JavaScript converts any string to a number. If we write 10=10, ‘a’ = 10 or ‘a’ = ‘a’, it will result in a reference error.ĭouble equals (=) is a comparison operator, which transforms the operands having the same type before comparison. This operator assigns lvalue to rvalue.įor example, Writing a=10 is fine. This.resetForm(this.getField("supervisor")) Įlse if(event.value != supV(event.Equal to (=) is an assignment operator, which sets the variable on the left of the = to the value of the expression that is on its right.

JAVASCRIPT DOES NOT EQUAL CODE
I tried this code with both the not equal (!=) and not equal value or type (!=) operators as well as leaving "event.value" out of calling the function and neither worked. This.getField("supervisor").value = getSupervisor.supervisor I left out the variables but below is a one line example of it. How would I go about this? If I take out lines 7-9 of the custom keystroke script, the script works except for the condition in which custom text is entered. I wanted to do this in the event the employee looks for their name but can't find it and it ends up populating with someone else's name. The code works and I've been using it for years, however I want to create a condition that states if the event value does not equal the function, it resets the supervisor combobox. I wanted to provision for new hires whose name may not be in the combobox yet. Both are comboboxes and both are set to allow the user to enter custom text. The end goal is to auto populate the employee's supervisor if the event will commit. I'm creating a form that lists employee names and using a document level function that calls an variable array in a custom keystroke script in a combobox.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
